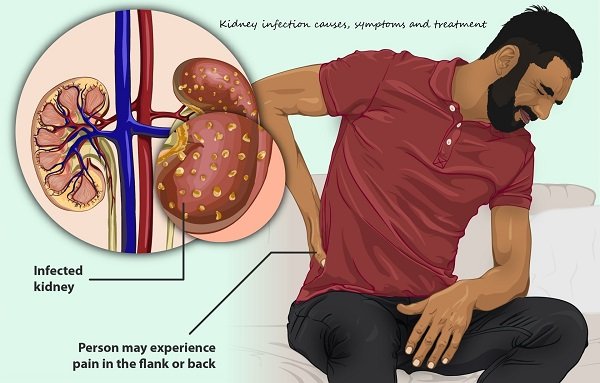
A kidney infection (pyelonephritis), is a painful and potentially serious condition that affects one or both kidneys. This occurs when bacteria travel from another part of the urinary tract, like the bladder or urethra, and infect the kidney.
The kidneys are organs that filter waste and extra fluid from the blood. They also help regulate the blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production. A kidney infection can damage the kidneys and cause other complications if not treated promptly.
What causes kidney infections in both male and females? |
Kidney infections are caused by bacteria and viruses . They enter the urinary tract through the urethra and travel to the kidneys. They can also spread from another part of the body through the bloodstream to the kidneys. The bacteria can multiply in the kidneys, causing inflammation and infection.
Viruses can also cause kidney infections, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems. |
Bacteria are the most common cause of kidney infections. They are bacteria that normally live in the intestines, then enter the urinary tract through the urethra and travel to the bladder and then the kidneys. Common bacteria that cause kidney infections include E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
What are the early warning signs and symptoms of kidney infections? |
⦁ A burning feeling or pain when urinating
⦁ Chills
⦁ Urine that smells bad or is cloudy
⦁ Having to urinate often
⦁ Fever
⦁ Nausea and vomiting
⦁ A strong, lasting urge to urinate
⦁ Back, side or groin pain
⦁ Pus or blood in the urine
⦁ Belly pain
Risk factors that can increase your risk of developing a kidney infection include: |
⦁ Being female: Women have a shorter urethra than men, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder and travel to the kidneys. The urethra is also close to the vagina and anus, where bacteria can be present.
⦁ Having a urinary tract blockage: Anything that slows down the flow of urine or prevents you from emptying your bladder completely can increase the risk of a kidney infection. This can be caused by a kidney stone, an enlarged prostate, a narrowed urethra, or a birth defect.
⦁ Having diabetes: Diabetes can damage nerves in the bladder, leading to incomplete emptying and increasing the risk of infection.
⦁ Having a recent urinary tract infection: UTI can increase the risk of bacteria traveling to the kidneys, especially if they were not treated properly, you are more likely to get a kidney infection. |
⦁ Having a weakened immune system: Conditions that weaken your immune system, such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or certain medications, can make you more prone to infections and this make it harder for your body to fight off infection.
⦁ Being pregnant: Pregnancy can change the anatomy of the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infection.
How is a kidney infection diagnosed? |
Diagnosis of a kidney infection is based on the symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and urine and blood tests.
Your health care provider may also order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an X-ray, to check for any abnormalities in your kidneys or urinary tract.
The fastest way to flush and treat kidney infections without antibiotics? |
The treatment of a kidney infection depends on the severity of your condition and the type of bacteria causing the infection.
Beyond antibiotics: Exploring supplementary approaches.
Fortunately, we have an effective treatment options available to help you recover quickly, alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Here's your one-stop treatment supplements to effectively clear off kidney infections, helping you reclaim your health and well-being.